- About MAA
- Membership
- MAA Publications
- Periodicals
- Blogs
- MAA Book Series
- MAA Press (an imprint of the AMS)
- MAA Notes
- MAA Reviews
- Mathematical Communication
- Information for Libraries
- Author Resources
- Advertise with MAA
- Meetings
- Competitions
- Programs
- Communities
- MAA Sections
- SIGMAA
- MAA Connect
- Students
- MAA Awards
- Awards Booklets
- Writing Awards
- Teaching Awards
- Service Awards
- Research Awards
- Lecture Awards
- Putnam Competition Individual and Team Winners
- D. E. Shaw Group AMC 8 Awards & Certificates
- Maryam Mirzakhani AMC 10 A Awards & Certificates
- Two Sigma AMC 10 B Awards & Certificates
- Jane Street AMC 12 A Awards & Certificates
- Akamai AMC 12 B Awards & Certificates
- High School Teachers
- News
You are here
Leonardo of Pisa: Bunny Rabbits to Bull Markets - Golden Ratio
If you actually divide successive terms in the Fibonacci sequence, the quotients settle down to a specific value as you can see in the table below.
| 1/1 | = 1 | 2/1 | = 2 | |||
| 3/2 | = 1.5 | 5/3 | = 1.666... | |||
| 8/5 | = 1.6 | 13/8 | = 1.625 | |||
| 21/13 | = 1.61538... | 34/21 | = 1.61904 | |||
| 55/34 | = 1.61764 | 89/55 | = 1.61818 | |||
| 144/89 | = 1.61798 | 233/144 | = 1.61805 | |||
| 377/233 | = 1.61802 | 610/377 | = 1.61803 | |||
The quotients approach a number called the Golden Ratio whose value can be calculated algebraically. Using conventional subscript notation, the Fibonacci sequence is defined:
f1 = f2 = 1, fn+1 = fn + fn-1, n = 2, 3, ....
Now, the Golden Ratio is usually called . We say fn+1/fn → as n → ∞. Noting that both fn+1/fn and fn /fn-1 have the same limit as n → ∞, the calculation goes like this:
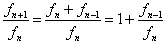 |
||
|
Now replace the two terms: fn+1/fn with the variable x and fn-1/fn with 1/x. |
||
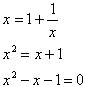 |
||
|
This quadratic equation has the two solutions: |
||
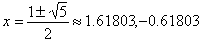 |
||
The first solution is the Golden Ratio , and the second is just - 1/ !
Why is this ratio golden? That's really hard to say. It is definitely related to the pleasing nature of the proportion and the uncanny way it pops up in architecture and art; for example, we find the ratio in:
- Proportions in Leonardo da Vinci's Mona Lisa
- Rectangles in Piet Mondrian's Composition 10
Many people claim that the ratio also appears in the Parthenon, in Athens. Unfortunately, it is not possible to determine the original measurements of the building due to its partial destruction over the centuries.
Sandra Monteferrante, "Leonardo of Pisa: Bunny Rabbits to Bull Markets - Golden Ratio," Convergence (August 2011)





